Astrophotography Filter
H-Beta (Hb) Filter for DSLR Camera
H-Beta (Hb) Filter for DSLR Camera
FREE SHIPPING
Couldn't load pickup availability
H-Beta Filter for DSLR Camera
Unlock the Universe with the H-Beta (Hb) Filter for DSLR Camera
The H-Beta (Hb) Filter for DSLR Camera is your gateway to capturing the mesmerizing beauty of the cosmos. Engineered with precision, this filter isolates the H-beta spectral line at 486nm, allowing you to capture the subtle nuances and intricate details of nebulae and deep-sky objects that may be invisible to the naked eye or with standard camera lenses.
Revealing Hidden Details
The Hydrogen Beta Filter is specially designed to reveal hidden details in your astrophotography. By isolating the H-beta spectral line at 486nm, this filter allows you to capture the intricate structures and subtle nuances of nebulae and other deep-sky objects. This unique capability makes it an essential tool for astrophotographers seeking to capture the ethereal beauty of the universe with unparalleled clarity and detail.
Minimizing Light Pollution
Light pollution is a common challenge for astrophotographers, especially those in urban environments. The H-Beta Filter features a narrow bandpass design that effectively filters out unwanted light pollution, resulting in clearer and more vibrant images of the night sky. This enables you to capture celestial phenomena with greater contrast and clarity, even in light-polluted areas.
Enhancing Compatibility
Designed with a photo round frame and equipped with a sturdy metal screw thread, the Hydrogen Beta Filter seamlessly integrates with a wide range of camera lenses. This ensures optimal compatibility and hassle-free attachment, providing flexibility in your astrophotography endeavors. Whether you are using a prime lens or a zoom lens, the H-Beta Filter is designed to fit perfectly and deliver exceptional performance.
Unlocking Astrophotography Potential
By investing in a Hydrogen Beta Filter, you are unlocking the potential to capture breathtaking images of the cosmos with unmatched clarity and detail. Whether you are a seasoned astrophotographer or a passionate enthusiast, this filter empowers you to capture the wonders of the universe and take your photography to new heights.

Observing Celestial Objects with H-Beta Emission
Hydrogen Beta (H-beta) emission can be found in various celestial objects throughout the universe, particularly in regions where hydrogen gas is ionized and emits light at a specific wavelength of 486nm. Here are some examples of where H-beta emission can be observed:
Nebulae
Nebulae are vast clouds of interstellar gas and dust where star formation occurs. H-beta emission is commonly observed in emission nebulae, such as the Orion Nebula (M42), the Lagoon Nebula (M8), and the Eagle Nebula (M16). These nebulae contain ionized hydrogen gas that emits light in the H-beta spectral line, revealing the vibrant colors and intricate structures of these cosmic clouds.
Supernova Remnants
Supernova remnants are the remnants of massive stars that have exploded at the end of their life cycles. H-beta emission can be detected in the expanding shells of gas ejected during the supernova explosion. Examples of supernova remnants with prominent H-beta emission include the Veil Nebula (NGC 6960) and the Crab Nebula (M1).
Planetary Nebulae
Planetary nebulae are the glowing shells of gas ejected by dying stars during the later stages of their evolution. H-beta emission is often observed in the ionized gas surrounding these stars. Examples of planetary nebulae with H-beta emission include the Helix Nebula (NGC 7293) and the Dumbbell Nebula (M27).
Galactic H II Regions
H II regions are regions of ionized hydrogen gas found within galaxies, often associated with regions of active star formation. H-beta emission is prevalent in these regions due to the presence of hot, young stars that ionize the surrounding gas. Examples of galactic H II regions include the Tarantula Nebula in the Large Magellanic Cloud and the H II regions within the spiral arms of the Milky Way galaxy.
Benefits of Using a Camera Lens for Astrophotography
Using a camera lens for astrophotography, especially in conjunction with specialized filters like the Hydrogen Beta (H-beta) Filter, offers several benefits:
Versatility in Focal Lengths
Camera lenses provide a wide range of focal lengths, allowing photographers to capture a variety of celestial objects, from wide-field views of the night sky to detailed shots of distant galaxies and nebulae. This versatility enables photographers to capture different aspects of astrophotography with a single piece of equipment.
Ease of Use
Camera lenses are typically lightweight and easy to set up, making them ideal for astrophotographers of all skill levels. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced photographer, using a camera lens simplifies the process of capturing stunning images of the night sky.
Portability
Camera lenses are compact and portable, making them convenient for astrophotographers who prefer to travel to remote locations for optimal viewing conditions. With a camera lens, you can easily pack your equipment and venture into the wilderness to capture breathtaking shots of the cosmos.
High-Quality Optics
Many camera lenses are equipped with high-quality optics that deliver sharpness and clarity across the frame, even when shooting wide open apertures. This ensures that astrophotographers can capture detailed images of celestial objects with minimal distortion or aberrations.
Compatibility with Filters
Camera lenses can be easily paired with specialized filters like the H-beta Filter to enhance astrophotography capabilities. Filters such as the H-beta Filter isolate specific wavelengths of light emitted by celestial objects, allowing photographers to capture stunning images with enhanced contrast and detail.
Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to dedicated astronomical telescopes, camera lenses are often more affordable options for astrophotography enthusiasts. By utilizing a camera lens with specialized filters, photographers can achieve impressive results without breaking the bank.
The H-Beta Filter: Technical Specifications and Design
The H-Beta Filter is meticulously engineered to deliver outstanding performance in astrophotography. Here are the key technical specifications and design features:
Filter Type: H-Beta
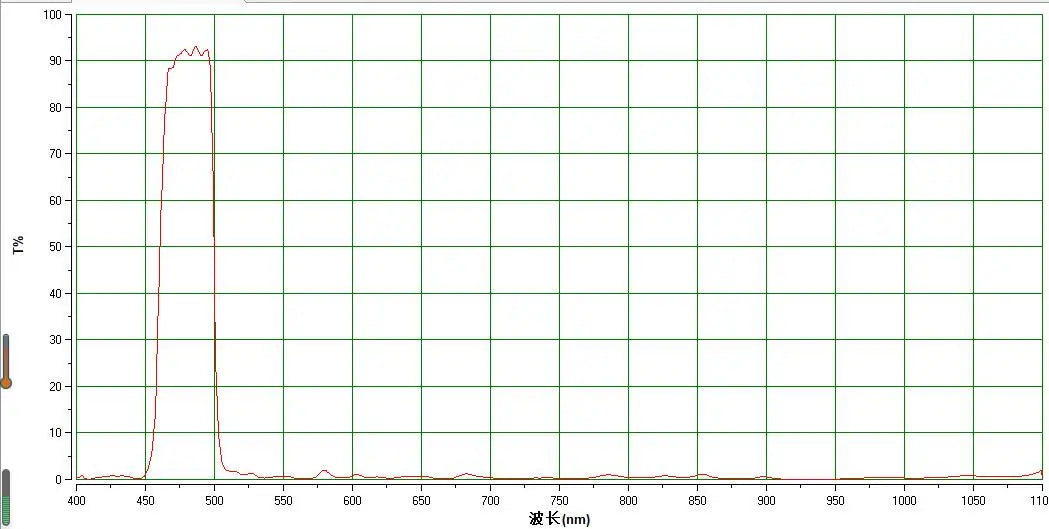
Spectral Line: 486nm
Bandpass Design: Narrow
Frame Type: Photo Round
Frame Material: Metal
Available Sizes: 48mm, 49mm, 52mm, 55mm, 58mm, 62mm, 67mm, 72mm, 77mm, 82mm
Compatibility: Various camera lenses
Applications: Astrophotography, Nebula Imaging, Deep-Sky Object Observation
Package Contents: 1x H-Beta (Hb) Filter for DSLR Camera, Protective Case
Capturing the Beauty of the Universe with the H-Beta Filter
Designed to elevate your astrophotography experience, the H-Beta Filter is meticulously crafted for capturing celestial moments in the darkest of nights. Its ability to filter out light pollution ensures that your images are clear and vivid, allowing you to immerse yourself in the beauty of the universe with every shot.
Secure Attachment for Hassle-Free Shooting
The H-Beta Filter features a sturdy metal screw thread that guarantees a secure attachment to your camera lens. This ensures stability during your astrophotography sessions, allowing you to focus on capturing the mesmerizing beauty of the universe without any distractions.
Ideal for Nebula Imaging and Deep-Sky Observation
The H-Beta Filter is particularly well-suited for nebula imaging and deep-sky observation. Its narrow bandpass design isolates the H-beta spectral line, making it possible to capture the intricate details and vibrant colors of nebulae and other celestial phenomena. This makes the filter an essential tool for astrophotographers seeking to capture the ethereal beauty of the universe with unparalleled clarity and detail.
High-Quality Materials for Durability
Crafted from high-quality materials, the H-Beta Filter is designed to withstand the rigors of outdoor use. The metal frame ensures durability and longevity, while the protective case included in the package keeps the filter safe when not in use. This makes the H-Beta Filter a reliable and long-lasting addition to your astrophotography gear.
Why Should I Use a Hydrogen Beta Filter?
Using a Hydrogen Beta (H-beta) Filter in your astrophotography endeavors brings numerous advantages, allowing you to capture the night sky with exceptional detail and clarity. Here’s why you should consider adding this specialized filter to your photography gear:
1. Reveal Hidden Details
The Hydrogen Beta Filter isolates the H-beta spectral line at 486nm, which is crucial for capturing the faint and intricate details of nebulae and other deep-sky objects. Standard camera lenses often miss these subtle nuances, but the H-beta filter brings them to the forefront, allowing you to photograph the fine structures and vibrant hues of cosmic clouds that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye.
2. Minimize Light Pollution
Light pollution is a significant challenge for astrophotographers, particularly those shooting in urban areas. The H-beta filter features a narrow bandpass design that effectively filters out unwanted light pollution, resulting in clearer and more vibrant images. This enables you to photograph celestial phenomena with greater contrast and clarity, even in less-than-ideal conditions.
3. Enhance Compatibility and Flexibility
The H-beta filter is designed with a photo round frame and equipped with a sturdy metal screw thread, ensuring it seamlessly integrates with a wide range of camera lenses. This compatibility provides flexibility, allowing you to use the filter with various camera setups and switch between lenses effortlessly. Whether you are using a wide-angle lens for broad sky views or a telephoto lens for detailed shots of specific objects, the H-beta filter adapts to your needs.
4. Cost-Effective Solution
Compared to dedicated astronomical telescopes, camera lenses paired with the H-beta filter offer a more affordable solution for astrophotography enthusiasts. You can achieve impressive results without the high cost associated with specialized telescopes, making astrophotography accessible to a broader range of photographers.
5. Capture Astounding Astrophotography
The H-beta filter unlocks the potential to capture breathtaking images of the cosmos with unparalleled clarity and detail. Whether you are a seasoned astrophotographer or a passionate beginner, this filter empowers you to photograph the wonders of the universe and take your photography to new heights. The stunning images you capture will not only be clearer but also rich in contrast and color, providing a truly immersive visual experience.
6. Durability and Longevity
Crafted from high-quality materials, the H-beta filter is built to withstand the rigors of outdoor use. The metal frame ensures durability, while the protective case keeps the filter safe when not in use. This longevity makes the H-beta filter a reliable and long-lasting addition to your astrophotography gear, providing value for years to come.
Where Can Hydrogen Beta Be Found in Space?
Hydrogen Beta (H-beta) emission can be found in various celestial objects throughout the universe, particularly in regions where hydrogen gas is ionized and emits light at a specific wavelength of 486nm. Here are some prominent examples of where H-beta emission can be observed:
1. Nebulae
Nebulae are vast clouds of interstellar gas and dust where star formation occurs. H-beta emission is commonly observed in emission nebulae, which are regions of active star formation and ionized gas. Examples of nebulae with prominent H-beta emission include:
- Orion Nebula (M42): One of the brightest and most well-known emission nebulae, the Orion Nebula is a stellar nursery where new stars are born. The ionized hydrogen gas in this nebula emits light in the H-beta spectral line, revealing its vibrant colors and intricate structures.
- Lagoon Nebula (M8): Located in the constellation Sagittarius, the Lagoon Nebula is another region of intense star formation, showcasing prominent H-beta emission.
- Eagle Nebula (M16): Famous for the "Pillars of Creation" captured by the Hubble Space Telescope, the Eagle Nebula contains regions of ionized hydrogen that emit H-beta light, revealing its majestic structures.
2. Supernova Remnants
Supernova remnants are the expanding shells of gas and dust ejected during the explosive death of a massive star. H-beta emission can be detected in these remnants, providing insights into the composition and dynamics of the ejected material. Examples of supernova remnants with significant H-beta emission include:
- Veil Nebula (NGC 6960): Part of the Cygnus Loop, the Veil Nebula is a supernova remnant that exhibits beautiful H-beta emission, highlighting the intricate filaments of ionized gas.
- Crab Nebula (M1): The result of a supernova explosion observed in 1054 AD, the Crab Nebula is a well-studied supernova remnant with prominent H-beta emission.
3. Planetary Nebulae
Planetary nebulae are the glowing shells of gas ejected by dying stars during the later stages of their evolution. H-beta emission is often observed in the ionized gas surrounding these stars. Examples of planetary nebulae with H-beta emission include:
- Helix Nebula (NGC 7293): Often referred to as the "Eye of God," the Helix Nebula is a large planetary nebula with striking H-beta emission.
- Dumbbell Nebula (M27): Located in the constellation Vulpecula, the Dumbbell Nebula is another example of a planetary nebula with significant H-beta emission.
4. Galactic H II Regions
H II regions are regions of ionized hydrogen gas found within galaxies, often associated with regions of active star formation. H-beta emission is prevalent in these regions due to the presence of hot, young stars that ionize the surrounding gas. Examples of galactic H II regions include:
- Tarantula Nebula: Located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, the Tarantula Nebula is one of the most active star-forming regions in our local group of galaxies, with intense H-beta emission.
- H II Regions in the Milky Way: The spiral arms of our galaxy, the Milky Way, contain numerous H II regions where H-beta emission can be observed. These regions are often associated with massive star-forming complexes.
Using a Hydrogen Beta Filter in your astrophotography allows you to capture the night sky with exceptional detail and clarity, revealing hidden details, minimizing light pollution, and enhancing the compatibility and flexibility of your camera lenses. Hydrogen Beta emission can be found in various celestial objects, including nebulae, supernova remnants, planetary nebulae, and galactic H II regions, providing valuable insights into the dynamics and composition of these cosmic phenomena. By adding the H-beta filter to your astrophotography gear, you can unlock the full potential of your DSLR camera and capture the wonders of the universe in stunning detail.
Upgrade Your Astrophotography Gear Today
Elevate your astrophotography game with the H-Beta Camera Lens Filter—where cutting-edge technology meets the beauty of the universe. Uncover the mysteries of the night sky and capture breathtaking celestial moments with unparalleled clarity. Upgrade your gear today and let the cosmos come to life through your lens.
H-Beta (Hb) Filter for DSLR Camera Lens
The H-Beta (Hb) Filter for DSLR Camera is an essential accessory for any astrophotographer looking to capture the ethereal beauty of the universe with unmatched clarity and detail. Engineered with precision and designed for optimal compatibility, this filter isolates the H-beta spectral line at 486nm, making it possible to capture the intricate details of nebulae and other deep-sky objects. With its narrow bandpass design, the H-Beta Filter effectively filters out unwanted light pollution, ensuring crisp and clear images of the night sky. Whether you are a seasoned astrophotographer or a passionate enthusiast, the H-Beta Filter is your gateway to capturing the wonders of the cosmos with unparalleled clarity and detail. Upgrade your astrophotography gear today and unlock the full potential of your DSLR camera with the H-Beta Filter.
Share